What is thyroid?
Thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland that lies at the lower front part of the neck, below the Adam’s apple. The thyroid gland produces thyroid hormones that regulate our metabolism, growth, development and body temperature.

Symptoms
Thyroid cancer commonly presented as a painless, palpable thyroid lump on the neck. Patients and doctors discover most of these lumps during examination of the neck. A thyroid gland can look larger than normal either due to generally enlarged gland or due to enlarged nodules in it. Solitary nodules are most likely to be malignant in patients older than 60 years or younger than 30 years. Malignant nodules are usually painless, and a fast-growing nodule may suggest malignancy. Thyroid nodules are associated with higher risk of malignancy in male.
Not all thyroid nodules are dangerous, benign thyroid nodules are more common than malignant. Thus, a patient with thyroid swelling needs to consult his or her doctor for further assessment of the swelling.
Evaluation
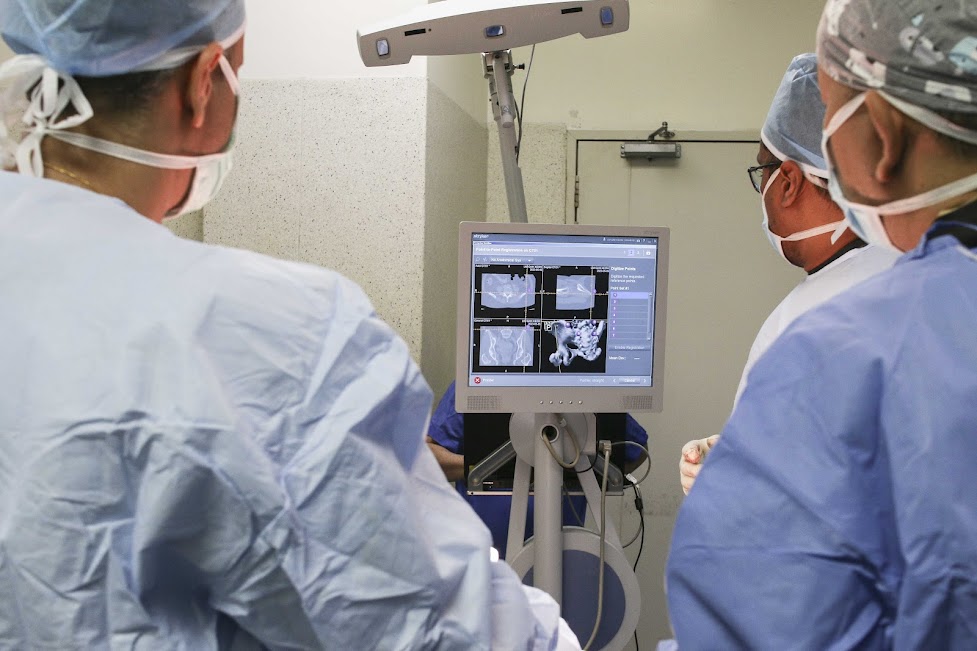
Fine needle aspiration biopsy is the most important tool in evaluating thyroid nodules. It is easy to perform with only few minor possible complications. The purpose of this procedure is to study the cells in the thyroid nodules.
Ultrasonography is the most common scan is evaluating thyroid swelling. In certain occasions, CT scans, MRI scans may be needed to assess the extent of the tumour, lymph node involvement and tumour spread.
Types of thyroid cancer
There are 4 main types of thyroid cancer
1. Papillary thyroid cancer
The most common form of well-differentiated thyroid cancer. Papillary cancer has a propensity to invade lymphatics but less likely to invade blood vessels.
2. Follicular thyroid cancer
The second most common thyroid cancer. Follicular cancer may spread to other organs. Patients with follicular cancer are more likely to develop lung and bone metastases than patients with papillary cancer.
(Papillary and follicular thyroid cancer are differentiated thyroid cancer, together they make up about 95% of thyroid cancers. The prognosis of this cancer is related to age, it is better for younger patients than for patients who are older than 45 years old. With appropriate treatment, a young female patient whose cancer does not extend beyond the capsule of the gland, life expectancy is minimally affected.)
3. Medullary thyroid cancer
Medullary thyroid cancer arises from C cells of the thyroid, and it produces calcitonin, which can be used as a tumour marker. It does not accumulate radioiodine. It can appear sporadically or can be part of an inherited disorder named Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Type 2 (MEN2).
4. Anaplastic thyroid cancer
The most aggressive type of thyroid cancer. Even though it accounts for less than 2% of thyroid cancer, it causes up to 40% of deaths from thyroid cancer.
Treatment
Thyroid cancers require surgical intervention whenever possible. After surgery, for patients with papillary and follicular cancers, they undergo radioiodine scanning and radioablation of any residual disease.
If you experience any signs or symptoms mentioned above, please make appointment with you doctor.