Definition
Overweight and obesity are defined as abnormal or excessive fat accumulation that presents a risk to health.
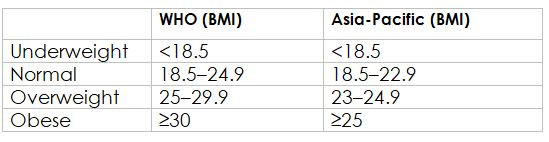
- Overweight is a BMI greater than or equal to 25
- Obesity is a BMI greater than or equal to 30
Body mass index (BMI) is a simple index of weight for height that is commonly used to classify overweight and obesity in adults.

It is defined as a person’s weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters (kg/m2).
Obesity classification according to WHO and Asia-Pacific guidelines
Why the Asian BMI cut-off is lower
Asians have a higher risk of Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease at BMIs lower than the existing WHO cut-off point for overweight (⩾25 kg/m2), possibly due to higher body fat percentage compared to Europeans.
Malaysian Data:
According to the 2019 Malaysian National Health and Morbidity Survey, 50.1% of adults are overweight or obese (30.4% overweight and 19.7% obese)
What causes obesity and overweight?
They are mainly caused by an energy imbalance between calories consumed and calories expended, due to:
- An increased intake of energy-dense foods: ultra-processed foods, foods that are high in fat and sugars
- Physical inactivity
There are other factors that influence this such as environmental, education, economy and health policies.
What are the common health consequences of being overweight and obese?
Overweight and obesity is a major risk factor for many non-communicable diseases mainly:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Diabetes
- Musculoskeletal disorders- osteoarthritis
- Some cancers (including endometrial, breast, ovarian, prostate, liver, gallbladder, kidney, and colon)
The higher the BMI, the higher the risk.
How can overweight and obesity be reduced?
Supportive environments and health education can help people make healthier choices about food and encourage regular physical activity.
- Limit intake of harmful fats, added sugars and ultra-processed foods
- Increase consumption of fruit and vegetables, as well as legumes, whole grains and nuts
- Engage in regular physical activity (150 minutes a week for adults)
Reference: WHO-Obesity