Ear, Nose and Throat (Otorhinolaryngology)
08/06/2021
6 minutes read

Tobacco smoke can cause cancer at different site of our human body, including lungs, oral cavity (mouth), throat, nose etc. Commonly we know that tobacco smoking causes lung cancer (lower respiratory tract), but do you know that nose, mouth and throat which form upper airway (known as upper respiratory tract and digestive tract) are equally affected by tobacco smoke also. Mouth and Throat Cancer had contributed 30% and 35% of total cancer-related death in developed countries and developing countries respectively. Smokers are not the only one who can get cancer from tobacco smoke. People around them—their kids, partners, friends, co-workers, and others—breathe in that smoke known as second hand smoke, are at high risk of becoming cancer victims too.
Tobacco itself has released more than 5000 chemicals and at least 70 chemicals that can cause cancer, they are also known as carcinogens.

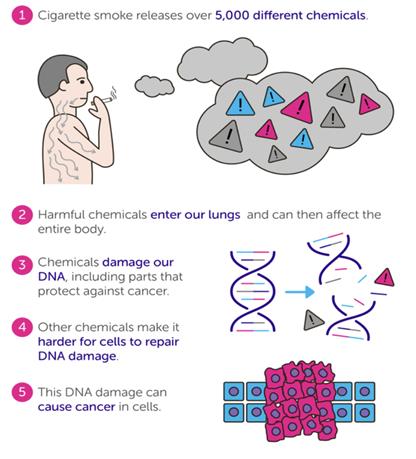
Each time we breathe in cigarette smoke, these chemicals get into our bloodstream and travelled to all parts of our body. These chemicals can damage our DNA (which controls our body new cells generation) and also damage DNA parts that protect against cancer.
The worst part is the devastating link between tobacco products and human cancers result from a powerful alliance of two components--nicotine and carcinogens. Without either one of these, tobacco would be just another commodity, instead of being the single greatest cause of cancer death. In fact, Nicotine is addictive and toxic, but it is not a carcinogen. This addictive behavior of continuous smoking of tobacco products use (contain numerous carcinogens) lead to constant exposure of our body parts to carcinogens which resulting in mouth and throat cancer, next to lung cancer.
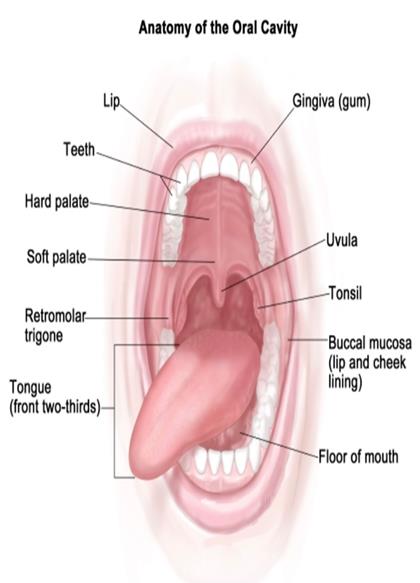
ORAL/MOUTH CANCER
Oral/Mouth cancer was one of the least heard of cancers by the public with only 56% of the participants being aware, out of these, there was a 76% awareness of the link between smoking and oral cancer.
Survey shows lack of public awareness that cigarette smoking and/or tobacco consumption (chewing tobacco or ‘dip’) contributed to Mouth/Oral Cancer.
Oral/Mouth cancer occurs when the cells in the mouth begin to grow and divide at an abnormal rate. DNA is the information house in a cell that commands the functioning of a cell. When DNA starts to malfunction, the cells grow and divide irrationally.
Symptoms of Oral/Mouth Cancer:
- Lump(s) in mouth/oral cavity
- Non-healing oral ulcer or tongue ulcer
- Sore mouth or throat
- Repetitive mild to high-grade fever
- Difficulties and pain in swallowing food
- Mouth or gum bleed
- Tremendous weight loss (at least 5kg loss within 2 months)
- Jaw stiffness
- Ear pain
- Visible white or red patches in the mouth
With the above mentioned clinical presentations and detailed history of sickness from the patient, thorough medical examinations, blood tests, endoscopic assessment and series of CT Scans or PET Scans are carried out to confirm the diagnosis and the staging of cancer (Stage 1, 2, 3, 4 or Advance stage)
Early detection is the key to survival from oral/mouth cancer. Early stages of mouth/oral cancer (stage 1 to 3) can be completely removed by surgery with or without radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy. Most of the time, the prognosis is good and the survival rate is high.
Oral/mouth ulcer by nature spreading fast through the lymphatic system, when cancer spread to lymph nodes or neck region and distant organ, especially cancer of the floor of the mouth, or oral cancer reached the later stages (stage 4 and advanced stage), the prognosis will be very poor. For all these advanced stages of oral cancer, palliative treatment with surgery most often results in significant facial disfigurement and seriously compromised oral function.
Hence, poor survival rates are mostly linked to diagnosis at late stages of the cancer due to delay in seeking advice from a doctor.
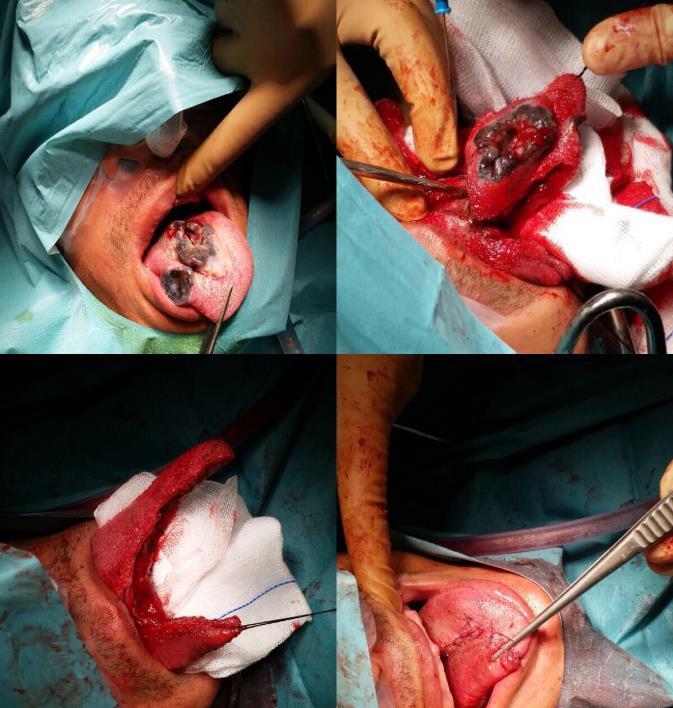
Tongue cancer with surgical removal and repair.
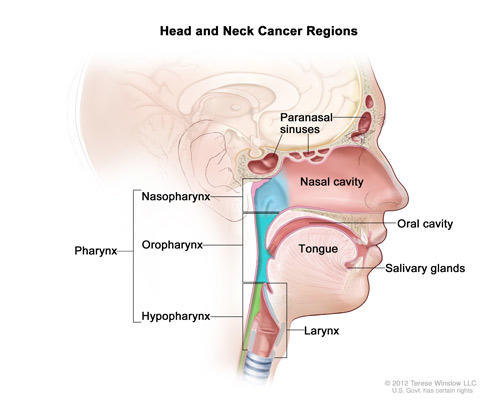
THROAT CANCER
The throat consists of 2 parts – Pharynx (a tube that starts behind our nose and ends in our neck) and Larynx (voice box). Throat (pharynx and larynx) cancer is strongly associated with tobacco smoking.
Doctors identify cancer by the location mentioned above:
1. Pharynx:
- Nasopharynx - upper part of throat behind the nose. It is one of the most common cancer in Malaysia.
- Oropharynx – located behind mouth. Cancer is most likely to grow in the tonsils (located at the back of the tongue) or the soft palate.
- Hypopharynx - the narrow area behind our voice box.
2. Larynx:
- Glottis - It holds our vocal cords.
- Supraglottis - above the glottis.
- Subglottis - area below our vocal cords and above our windpipe.
Symptoms of throat cancer:
- Hoarseness
- Shortness of breath
- Trouble swallowing (foreign body stuck sensation presence of foreign body sensation?)
- Sore throat, cough, or earache that won’t go away
- Headache
- Neck lump
- Unexplained weight loss.
Again, throat cancer is diagnosed and staged accordingly to stage 1, 2, 3, 4 or advanced stage based on clinical presentations as above mentioned, detailed of sickness history, thorough medical examinations, blood tests, endoscopic assessment and series of CT Scans or PET Scan.
Throat cancer is a common type of head and neck cancer due to cigarette smoking. Cancer tends to grow and spread quickly, therefore, early detection and treatment provide the best chance to beat them and to have a good quality of life.
The 5-year survival rate means the percentage of people who live at least 5 years after the cancer is diagnosed.
In Penang Adventist Hospital, there are a total of 113 cases of throat cancers being diagnosed over the past 10 years, which is equivalent to 20.9% of total head and neck cancers (540 cases) diagnosed. Out of 113 throat cancers, 67 (60%) were classified as early-stage (stage 1 to stage 3) throat cancer. All of the 67 cases were treated with radiotherapy with/without chemotherapy, the 5-year survival rate is as high as 90%.
39 out of 113 cases (34.5%) were diagnosed as stage-4 throat cancer. Despite the 2 defaulted-treatment cases, all of them received the treatment by undergoing major surgery known as laryngeal removal (partial or total laryngectomy, neck dissection, thyroid removal and pharyngeal repair, with permanent stoma at the front neck), the data shown 100% 5-year survival rate.
7 out of 113 (5.5%) cases that being diagnosed as advanced stage, normally presented clinically very ill condition like huge neck lump, hoarseness with difficulty in breathing and dramatic weight loss, cancer had spread to distant organs involving the lung and liver, the patient ceased few months after being diagnosed.
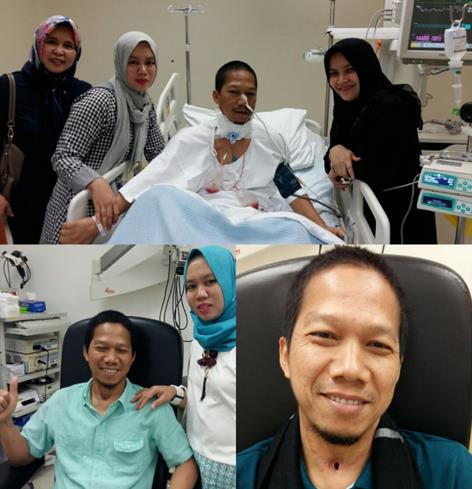
Throat cancer patient Post-op Day 1 (in ICU), one month and 3 months after surgery.
In conclusion, in early stages of throat cancer (stage 1, 2, and 3) and even stage 4, as long as no spreading to distant organs like liver, lung, brain or bone, the prognosis will be good with a high survival rate and restore back to normal life span.
This brings out a very clear message that public education in risk factors associated with Mouth and throat cancer is very important. Early detection of cancer and the necessity for fast track referral play the utmost important role. Recognition of oral and throat cancers in local strategies for oral, throat and neck health should be encouraged.
The final and most important message to avoid/prevent health risks from the mouth and/or throat cancer is:
- If you don’t smoke or use tobacco—don’t start!
- If you do smoke or use tobacco— do quit!
Based on WHO cancer data, it is evident that cancer is a critical global issue and all the countries must augment the key components of cancer control; cancer prevention, early detection, early diagnosis, adequate treatment and palliation. However, most of the increase in cancer incidence is not preventable, but many cancers cases can be effectively treated upon early diagnosis with very good outcome or prognosis.


